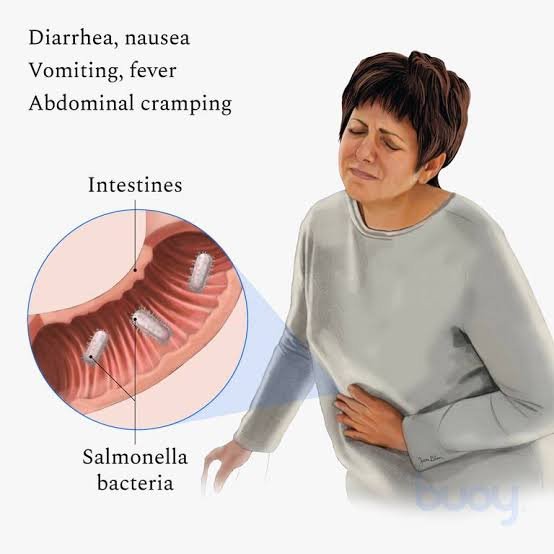
The Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is a type of bacterial infection caused by the Salmonella bacteria. It can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, it can lead to dehydration, blood infections, and even death.
Salmonella bacteria are commonly found in raw or undercooked meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products, as well as in fruits and vegetables that have been contaminated by animal feces. The bacteria can also be found on surfaces and in soil, water, and pet reptiles and birds.
To prevent salmonellosis, it is important to practice good food hygiene by washing hands and kitchen surfaces thoroughly, cooking meat and eggs thoroughly, and avoiding cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods. If you think you may have salmonellosis, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment, which may include antibiotics and fluid replacement therapy.
Salmonella bacteria are known for their ability to survive in a variety of environments, including the human digestive tract, which is why they can cause infection in humans. The symptoms of salmonellosis usually develop within 12 to 72 hours after exposure to the bacteria and can last for up to a week or more.
In most cases, salmonellosis is self-limiting, which means it will resolve on its own without medical treatment. However, in some cases, especially in people with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, young children, or those with certain medical conditions, salmonellosis can be severe and may require hospitalization.
In addition to the symptoms mentioned earlier, severe cases of salmonellosis can cause symptoms such as bloody stools, high fever, chills, headache, muscle pains, and fatigue. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis of salmonellosis is usually done through stool culture or blood tests to detect the presence of the bacteria. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, along with measures to manage the symptoms, such as hydration and electrolyte replacement.
To prevent salmonellosis, it is important to follow good food safety practices, including washing hands and kitchen surfaces thoroughly, cooking meat and eggs thoroughly, and avoiding cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods. It is also important to avoid consuming raw or undercooked eggs, meat, poultry, and seafood, and to properly handle and store food..
There are other measures that can be taken to prevent salmonellosis. These include avoiding contact with pet reptiles and birds, which can carry the bacteria on their skin and in their droppings. It is also important to avoid swimming in or drinking contaminated water, which can be a source of Salmonella infection.
If you have been diagnosed with salmonellosis, it is important to take precautions to avoid spreading the infection to others. This includes washing hands frequently with soap and water, avoiding contact with others while you are symptomatic, and avoiding preparing food for others until you have fully recovered.
In rare cases, Salmonella infection can lead to long-term complications, such as reactive arthritis or irritable bowel syndrome. However, most people who contract salmonellosis will recover fully without any long-term effects.
salmonellosis is a common bacterial infection that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. By following good food safety practices and taking other precautions to prevent infection, you can reduce your risk of contracting Salmonella and other foodborne illnesses.