Understanding the anatomy of the tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ located in the mouth that plays a vital role in the processes of taste, speech, and swallowing. It is made up of a complex network of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels that work together to enable its many functions.
The tongue is divided into several distinct parts. The tip of the tongue is the most anterior part and is responsible for precise movements that allow us to taste, speak, and manipulate food. The blade of the tongue, located behind the tip, is responsible for the movement of food from the mouth to the pharynx during swallowing. The body of the tongue, which is the largest part, is responsible for the formation of speech sounds, and the back of the tongue, known as the base or root, is responsible for swallowing.
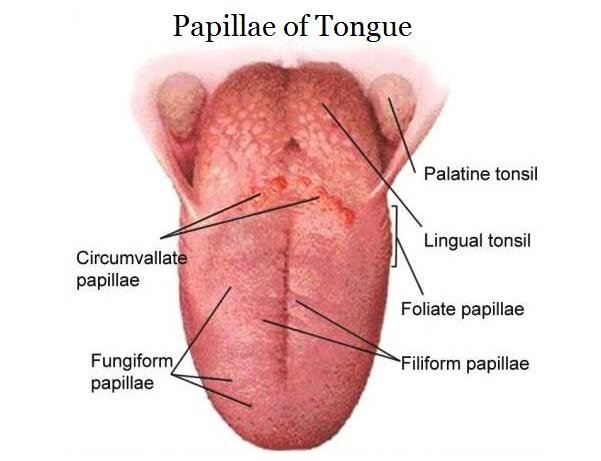
The tongue is covered with a layer of mucous membrane that is pink in color and has small bumps known as papillae. The papillae contain taste buds that allow us to taste the different flavors of food. The taste buds are responsible for detecting the five primary tastes: sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami (savory).
The tongue is also connected to the rest of the body through a complex network of nerves and blood vessels. The tongue is supplied with blood by the lingual artery, and the hypoglossal nerve controls its movements. The facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and vagus nerve are also involved in the functions of the tongue.
The tongue is a complex and versatile organ that plays a vital role in our ability to taste, speak, and swallow. Its many parts and functions work together seamlessly to enable us to communicate and enjoy the flavors of the food we eat.
In addition to its primary functions, the tongue also plays a significant role in maintaining oral health. The tongue's movements and actions help to clean the teeth, removing food particles and bacteria from the mouth. A healthy tongue is also important for preventing bad breath and promoting overall oral hygiene.
The tongue's appearance can provide valuable information about a person's overall health. A healthy tongue is typically pink, with a smooth surface and no visible lesions or discolorations. However, a white or yellow coating on the tongue can indicate an underlying health issue such as a fungal infection, while a red or inflamed tongue may be a sign of a vitamin deficiency or other health problem.
There are also several conditions that can affect the tongue, including tongue tie, geographic tongue, and oral cancer. Tongue tie, also known as ankyloglossia, is a condition in which the tongue's movement is restricted due to a shortened or thickened frenulum, the tissue that attaches the tongue to the bottom of the mouth. Geographic tongue is a condition in which the tongue's surface develops irregular patches that can change location over time. Oral cancer can also affect the tongue, and early detection is essential for effective treatment.
The tongue is a complex and fascinating organ that plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It enables us to communicate, enjoy the flavors of our food, and maintain oral health. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the tongue can help us to appreciate its importance and take better care of this essential part of our body.