INTERNET COMPUTER - Hype oder alles auf der Kette?
ICP: Eine neue Vision für das Internet
(3).png) Ki-Bild
Ki-Bild
Das Internet ist in den letzten Jahren zu einem zentralen Bestandteil unseres Lebens geworden. Wir nutzen es, um zu kommunizieren, zu arbeiten, zu lernen und zu unterhalten. Doch das Internet hat auch seine Schattenseiten. Es ist zentralisiert, anfällig für Zensur und Manipulation und nicht nachhaltig.
Internet Computer (ICP) ist ein neuer Ansatz für das Internet, der diese Probleme lösen soll. ICP ist eine dezentralisierte, skalierbare und nachhaltige Blockchain-Plattform, die es Entwicklern ermöglicht, Anwendungen zu erstellen, die auf der Blockchain ausgeführt werden.
Internet Computer, alles Onchain- Einzigartig
Die meisten Blockchain-Plattformen sind nicht vollständig onchain. Das bedeutet, dass sie einige Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausführen, z. B. die Speicherung von Daten oder die Ausführung von Smart Contracts.
Dies hat eine Reihe von Nachteilen.
Sicherheit: Wenn Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, sind sie anfälliger für Angriffe. Wenn Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, sind diese Funktionen nicht von diesen Sicherheitsfunktionen geschützt. Dies bedeutet, dass Angreifer diese Funktionen leichter manipulieren, betrügen oder hacken können.
Konkrete Beispiele für Sicherheitsprobleme:
Manipulation: Ein Angreifer könnte eine Funktion außerhalb der Blockchain manipulieren, um falsche Daten zu generieren oder Transaktionen zu fälschen.
Betrug: Ein Angreifer könnte eine Funktion außerhalb der Blockchain nutzen, um Benutzer zu betrügen, z. B. indem er ihnen falsche Informationen gibt oder ihnen Zugang zu ihren Daten verschafft.
Hacking: Ein Angreifer könnte eine Funktion außerhalb der Blockchain hacken, um Zugang zu sensiblen Daten oder Ressourcen zu erhalten.
Beispiele für Funktionen, die außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden:
Speicherung von Daten: Wenn Daten außerhalb der Blockchain gespeichert werden, sind sie nicht von der Blockchain-Sicherheit geschützt. Dies bedeutet, dass Angreifer diese Daten leichter manipulieren, betrügen oder hacken können. Ausführung von Smart Contracts: Wenn Smart Contracts außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, sind sie nicht von der Blockchain-Sicherheit geschützt. Dies bedeutet, dass Angreifer diese Smart Contracts manipulieren oder fälschen können, um Schaden anzurichten.
Authentifizierung und Autorisierung: Wenn Authentifizierung und Autorisierung außerhalb der Blockchain durchgeführt werden, sind sie nicht von der Blockchain-Sicherheit geschützt. Dies bedeutet, dass Angreifer sich leichter als andere Nutzer ausgeben oder Zugang zu sensiblen Daten erhalten können.
Dezentralisierung: Wenn Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, kann dies die Dezentralisierung der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Screenshot
Konkrete Beispiele für die Beeinträchtigung der Dezentralisierung durch die Ausführung von Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain:
Konzentration der Macht: Wenn eine bestimmte Partei die Kontrolle über die Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain hat, kann dies zu einer Konzentration der Macht auf dieser Partei führen. Dies kann die Dezentralisierung der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Anfälligkeit für Zensur: Wenn die Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain von einer zentralen Partei kontrolliert werden, kann diese Partei diese Funktionen zur Zensur von Inhalten oder Transaktionen verwenden. Dies kann die Dezentralisierung der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Unzuverlässigkeit: Wenn die Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain von einer zentralen Partei kontrolliert werden, kann diese Partei diese Funktionen unzuverlässig machen. Dies kann die Dezentralisierung der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Beispiele:
Wenn ein Unternehmen die Authentifizierung und Autorisierung seiner Nutzer außerhalb der Blockchain durchführt, kann dies dazu führen, dass das Unternehmen die Kontrolle über die Nutzerdaten hat. Dies kann die Dezentralisierung der Plattform beeinträchtigen, da die Nutzer ihre Daten nicht mehr selbst kontrollieren können.
Wenn ein Staat die Speicherung von Daten außerhalb der Blockchain durchführt, kann dies dazu führen, dass der Staat die Kontrolle über diese Daten hat. Dies kann die Dezentralisierung der Plattform beeinträchtigen, da die Nutzer ihre Daten nicht mehr selbst kontrollieren können.
Wenn ein Unternehmen die Ausführung von Smart Contracts außerhalb der Blockchain durchführt, kann dies dazu führen, dass das Unternehmen die Kontrolle über diese Smart Contracts hat. Dies kann die Dezentralisierung der Plattform beeinträchtigen, da die Nutzer nicht sicher sein können, dass die Smart Contracts ordnungsgemäß ausgeführt werden
Skalierbarkeit: Wenn Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, kann dies die Skalierbarkeit der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Konkrete Beispiele für die Beeinträchtigung der Skalierbarkeit durch die Ausführung von Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain:
Erhöhter Datenverkehr: Wenn Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, müssen die Daten dieser Funktionen über die Blockchain übertragen werden. Dies kann den Datenverkehr auf der Blockchain erhöhen und die Skalierbarkeit der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Erhöhte Rechenleistung: Wenn Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, müssen diese Funktionen von den Knoten der Blockchain ausgeführt werden. Dies kann die Rechenleistung der Knoten beanspruchen und die Skalierbarkeit der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Erhöhte Transaktionskosten: Wenn Funktionen außerhalb der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, müssen die Transaktionen dieser Funktionen auf der Blockchain durchgeführt werden. Dies kann die Transaktionskosten erhöhen und die Skalierbarkeit der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Beispiele:
Wenn ein Unternehmen die Authentifizierung und Autorisierung seiner Nutzer außerhalb der Blockchain durchführt, müssen die Nutzerdaten über die Blockchain übertragen werden. Dies kann den Datenverkehr auf der Blockchain erhöhen und die Skalierbarkeit der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Wenn ein Staat die Speicherung von Daten außerhalb der Blockchain durchführt, müssen diese Daten von den Knoten der Blockchain gespeichert werden. Dies kann die Rechenleistung der Knoten beanspruchen und die Skalierbarkeit der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Wenn ein Unternehmen die Ausführung von Smart Contracts außerhalb der Blockchain durchführt, müssen die Transaktionen dieser Smart Contracts auf der Blockchain durchgeführt werden. Dies kann die Transaktionskosten erhöhen und die Skalierbarkeit der Plattform beeinträchtigen.
Internet Computer ist hingegen vollständig onchain. Das bedeutet, dass alle Funktionen auf der Blockchain ausgeführt werden, einschließlich der Speicherung von Daten und der Ausführung von Smart Contracts.
Die Vorteile des Internet Computers
ICP bietet eine Reihe von Vorteilen gegenüber dem traditionellen Internet.
Dezentralisiert: ICP ist nicht von einer einzelnen Partei kontrolliert. Stattdessen wird er von einem Netzwerk von Knoten betrieben. Dies macht ihn widerstandsfähiger gegen Zensur und Manipulation.
Skalierbar: ICP ist in der Lage, eine große Anzahl von Transaktionen zu verarbeiten. Dies macht ihn für Anwendungen geeignet, die eine hohe Durchsatzleistung benötigen. Es sollen bis zu 100 000 Transaktionen möglich werden.
ICP Dashboard
Nachhaltig: ICP wird mit erneuerbarer Energie betrieben. Dies macht ihn zu einer nachhaltigeren Alternative zum traditionellen Internet.
Anwendungen des Internet Computers
Interner Computer kann für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen verwendet werden, darunter:
Dezentrale Anwendungen: ICP ist ideal für die Entwicklung dezentraler Anwendungen (dApps), die nicht von einer einzelnen Partei kontrolliert werden.
Skalierbare Anwendungen: ICP kann für Anwendungen verwendet werden, die eine hohe Durchsatzleistung benötigen, wie z. Spiele, soziale Medien und Finanzdienstleistungen.
Nachhaltige Anwendungen: ICP kann für Anwendungen verwendet werden, die nachhaltig sind, wie z. B. Blockchain-basierte Energienetze und intelligente Städte.
Energieeinsparung durch den Proof-of-DKG-Konsensus
Der Proof-of-DKG-Konsensus (Proof of Distributed Key Generation) ist ein verteilter Konsensalgorithmus, der für die Blockchain-Plattform Internet Computer (ICP) verwendet wird. Der Proof-of-DKG-Konsensus basiert auf der Idee, dass Knoten im Netzwerk eine gemeinsame Schlüsselmenge generieren müssen, um einen Konsens über einen neuen Block zu erzielen. Dieser Prozess erfordert keine große Rechenleistung, was den Proof-of-DKG-Konsensus energieeffizienter macht als andere Konsensalgorithmen wie Proof-of-Work.
Funktionsweise des Proof-of-DKG-Konsensus
Der Proof-of-DKG-Konsensus funktioniert wie folgt:
Die Validatoren im IC-Netzwerk generieren unabhängig voneinander verschiedene Schlüsselmengen.
Die Validatoren senden ihre Schlüsselmengen an einen anderen Knoten, den sogenannten Koordinator. Der Koordinator vergleicht die Schlüsselmengen und wählt eine gemeinsame Schlüsselmenge aus, die alle Validatoren akzeptieren.
Wenn eine gemeinsame Schlüsselmenge gefunden wurde, wird ein neuer Block generiert und an das Netzwerk gesendet.
Zur Zeit verbrauchen alle Nodes ca. 348 KW/h, wie man an der Grafik unten sehen kann Tendenz sinkend. 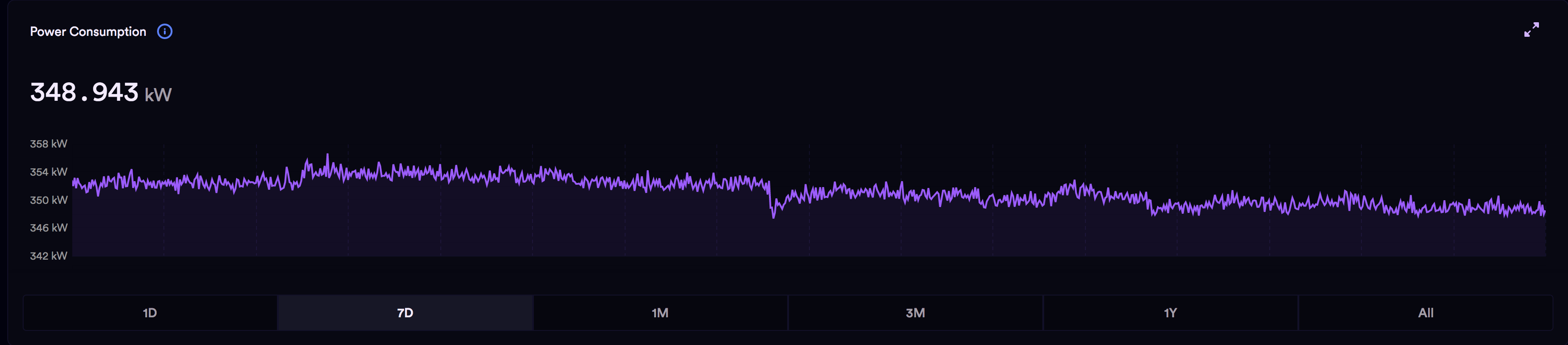 Screenshot ICP Dashboard
Screenshot ICP Dashboard
Umweltfreundlicher durch die Nutzung erneuerbarer Energien
ICP wird von einem Netzwerk von Knoten betrieben, die sich auf der ganzen Welt befinden. Die DFINITY Foundation, die den IC entwickelt, hat sich verpflichtet, die Energieversorgung des ICs mit erneuerbaren Energien sicherzustellen.
Dies trägt dazu bei, die Umweltauswirkungen von ICP weiter zu reduzieren.
Die Zukunft von Internet Computer
ICP ist noch in der frühen Entwicklungsphase. Doch es hat das Potenzial, das Internet grundlegend zu verändern.
Wenn ICP erfolgreich ist, könnte er zu einem dezentralisierten, skalierbaren und nachhaltigen Internet führen.
Hier ist einVideo von @jerrybanfield zu Internet Computer ( leider nur auf Englisch )
ICP: A new vision for the Internet
The Internet has become a central part of our lives in recent years. We use it to communicate, work, learn and entertain ourselves. But the internet also has its downsides. It is centralised, prone to censorship and manipulation and unsustainable.
Internet Computer (ICP) is a new approach to the Internet that aims to solve these problems. ICP is a decentralised, scalable and sustainable blockchain platform that enables developers to create applications that run on the blockchain.
Internet Computer, all onchain- Unique
Most blockchain platforms are not fully onchain. This means that they perform some functions outside of the blockchain, such as storing data or executing smart contracts.
This has a number of disadvantages.
Security: When functions are performed outside the blockchain, they are more vulnerable to attacks. When functions are executed outside the blockchain, these functions are not protected by these security features. This means that attackers can manipulate, cheat or hack these functions more easily.
Specific examples of security problems:
Manipulation: An attacker could manipulate a function outside the blockchain to generate false data or falsify transactions.
Fraud: An attacker could use a function outside the blockchain to defraud users, e.g. by giving them false information or giving them access to their data.
Hacking: An attacker could hack a function outside the blockchain to gain access to sensitive data or resources.
Examples of functions that are executed outside the blockchain
Storage of data: When data is stored outside the blockchain, it is not protected by blockchain security. This means that attackers can more easily manipulate, defraud or hack this data. Execution of smart contracts: When smart contracts are executed outside of the blockchain, they are not protected by blockchain security. This means that attackers can manipulate or forge these smart contracts to cause damage.
Authentication and authorisation: If authentication and authorisation are performed outside the blockchain, they are not protected by blockchain security. This means that attackers can more easily impersonate other users or gain access to sensitive data.
Decentralisation: If functions are executed outside the blockchain, this can impair the decentralisation of the platform.
Specific examples of how decentralisation can be impaired by performing functions outside the blockchain:
Concentration of power: If a particular party has control over the functions outside the blockchain, this can lead to a concentration of power on that party. This can affect the decentralisation of the platform.
Vulnerability to censorship: If the functions outside the blockchain are controlled by a central party, this party can use these functions to censor content or transactions. This can affect the decentralisation of the platform.
Unreliability: If the functions outside the blockchain are controlled by a central party, this party can make these functions unreliable. This can affect the decentralisation of the platform.
Examples:
If a company performs the authentication and authorisation of its users outside the blockchain, this can result in the company having control over the user data. This can affect the decentralisation of the platform, as users can no longer control their data themselves.
If a state stores data outside of the blockchain, this can lead to the state having control over this data. This can affect the decentralisation of the platform, as users can no longer control their data themselves.
If a company carries out the execution of smart contracts outside the blockchain, this may result in the company having control over these smart contracts. This can affect the decentralisation of the platform, as users cannot be sure that the smart contracts are executed properly
Scalability: If functions are executed outside the blockchain, this can impair the scalability of the platform.
Specific examples of how scalability is impaired by executing functions outside the blockchain
Increased data traffic: if functions are executed outside the blockchain, the data for these functions must be transferred via the blockchain. This can increase data traffic on the blockchain and affect the scalability of the platform.
Increased computing power: If functions are executed outside the blockchain, these functions must be executed by the nodes of the blockchain. This can consume the computing power of the nodes and impair the scalability of the platform.
Increased transaction costs: If functions are executed outside the blockchain, the transactions for these functions must be carried out on the blockchain. This can increase transaction costs and impair the scalability of the platform.
Examples:
If a company carries out the authentication and authorisation of its users outside the blockchain, the user data must be transferred via the blockchain. This can increase data traffic on the blockchain and impair the scalability of the platform.
If a state stores data outside the blockchain, this data must be stored by the nodes of the blockchain. This can consume the computing power of the nodes and affect the scalability of the platform.
If a company carries out the execution of smart contracts outside the blockchain, the transactions of these smart contracts must be carried out on the blockchain. This can increase transaction costs and impair the scalability of the platform.
Internet Computer, on the other hand, is completely onchain. This means that all functions are performed on the blockchain, including the storage of data and the execution of smart contracts.
The advantages of the Internet Computer
ICP offers a number of advantages over the traditional internet.
Decentralised: ICP is not controlled by a single party. Instead, it is operated by a network of nodes. This makes it more resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Scalable: ICP is capable of processing a large number of transactions. This makes it suitable for applications that require high throughput. Up to 100,000 transactions should be possible.

ICP Dashboard
Sustainable: ICP is powered by renewable energy. This makes it a more sustainable alternative to the traditional Internet.
Applications of the Internet Computer
Internal Computer can be used for a variety of applications, including:
Decentralised applications: ICP is ideal for developing decentralised applications (dApps) that are not controlled by a single party.
Scalable applications: ICP can be used for applications that require high throughput performance, such as gaming, social media and financial services.
Sustainable applications: ICP can be used for applications that are sustainable, such as blockchain-based energy grids and smart cities.
Energy savings through the Proof-of-DKG consensus
Proof-of-DKG consensus (Proof of Distributed Key Generation) is a distributed consensus algorithm used for the Internet Computer (ICP) blockchain platform. Proof-of-DKG consensus is based on the idea that nodes in the network must generate a common set of keys in order to reach consensus on a new block. This process does not require a large amount of computing power, which makes Proof-of-DKG consensus more energy efficient than other consensus algorithms such as Proof-of-Work.
Functionality of the Proof-of-DKG consensus
Proof-of-DKG consensus works as follows:
the validators in the IC network independently generate different sets of keys.
the validators send their key sets to another node, the so-called coordinator. The coordinator compares the key sets and selects a common key set that all validators accept.
if a common key set is found, a new block is generated and sent to the network.
Currently, all nodes consume approx. 348 KW/h, as you can see in the graph below. Screenshot ICP Dashboard
Screenshot ICP Dashboard
More environmentally friendly through the use of renewable energies
ICP is operated by a network of nodes located all over the world. The DFINITY Foundation, which is developing the IC, is committed to ensuring that the IC is powered by renewable energy.
This helps to further reduce the environmental impact of ICP.
The future of the Internet Computer
ICP is still in the early stages of development. But it has the potential to fundamentally change the Internet.
If ICP is successful, it could lead to a decentralised, scalable and sustainable internet.
Here is a video by @jerrybanfield on Internet Computing
Follow @lichtblick
Kannst du einen einfachen Smart Contract auf dem ICP vorführen?
Bei dem Konsens bin ich auch ziemlich skeptisch.
Grüße
Ja es geht z.B. auch ein Begrüssungssatz
Schauen wir mal was mit dem Konsens wird :-)
Geht auch ein echter 'Smart Contract' ?
Also quasi 'digitaler Vertrag' ?
Man macht einen Vertrag mit einem Gegenüber.. nicht mit sich selbst..
oder als Befehl für Begrüßungsnachrichten an einen Bot.
Ja, das geht auch.
!BEER
Thanks.