Injuries of the brachial plexus- why you lost sensation at the upper limb
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that are entwined with one another. It is responsible for controlling mobility and awareness in the arm and hand. An injury to the brachial plexus includes sudden damage to these nerves, which can result in discomfort, weakness, loss of sensation, or loss of mobility in the shoulder, arm, and/or hand.
The brachial plexus starts at the base of the neck and travels all the way down to the underarm, crossing the upper torso on the way. An injury to this network of nerves frequently occurs when your arm is forcefully pulled or stretched, or when your head and neck are forcibly dragged away from your shoulder. Both of these actions can also cause an injury to your shoulder.
Injuries to the brachial plexus that are not significant may heal on their own, but more serious injuries may necessitate surgical intervention for the patient to restore function in their arm or hand.
Injuries to the baby's brachial plexus can happen either while the baby is still in the uterus or while the baby is being delivered. This condition is referred to as prenatal brachial plexus paralysis when it occurs in infants (NBPP).
What exactly is meant by the phrase "brachial plexus"?
The brachial plexus is made up of five nerves that radiate out from the spinal cord at the level of the neck. These nerves are responsible for transmitting impulses from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm, and hand. On either side of your torso, you'll find your brachial plexus.
In the field of medicine, a plexus is a group of nerves, blood vessels, or lymphatic systems that cross each other in the body. Plexuses can also be found in animals. "Brachial" refers to something that is "of or of the arm or to a component that resembles the arm" (the brachial artery, for example, is the main vessel supplying blood to the muscles in your upper arm and elbow joint). Therefore, the brachial plexus is a collection of neurons that extends from the base of your spinal column down into your arm.
These five nerves are connected to the nerves that enable movement in the muscles of the arm and hand through a structure called the plexus. These nerves are also responsible for providing sensation to the epidermis.
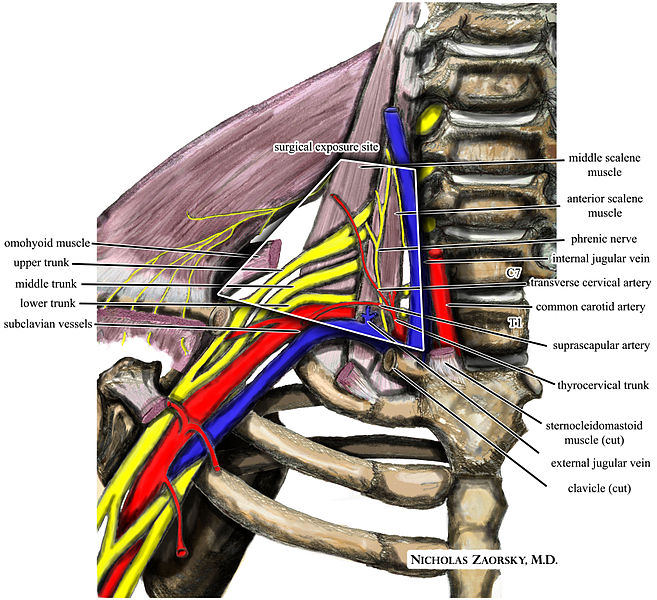
Wikipedia medical illustration thoracic outlet syndrome brachial plexus anatomy with labels.jpg - Wikimedia Commons. 2010, June 11. Wikimedia Commons.
Each of the five neurons that make up the brachial plexus serves a distinct purpose. Some of these functions include the stimulation of muscles, while others include the transmission of sensory information from the hand to the brain. Examples of this information include temperature and contact.
Because each nerve does something different, the symptoms you have and the treatment you may need depend on where the damaged nerve is in the plexus and what kind of nerve it is.
What are the different kinds of accidents that can occur to the brachial plexus?
The seriousness of brachial plexus injuries can range considerably from mild to severe, depending on the nature of the injury and the amount of force that was applied to it. A single incident can result in injuries of various degrees of seriousness to several different nerves in your brachial plexus.
Here are the most common types of injuries that can happen to the brachial plexus:
Stretch neuropraxia is a condition that happens when a nerve in the brachial plexus is stretched in a way that damages the nerve's protective covering. This results in disruptions in the normal transmission of nerve signals, but it does not necessarily cause injury to the nerve beneath the skin. It might get better on its own, but you might also need simple, non-surgical treatments like physical therapy to get back to normal.
Rapture: Rupture is the term used to describe the condition that occurs when a brachial plexus nerve is stretched more forcefully than it can withstand, causing it to rupture either partially or completely. Surgical intervention is typically necessary to restore injuries of this nature.
Avulsion injury to the brachial plexus is the most serious kind of damage that can occur to this area. This health problem happens when a nerve fiber breaks away from the spinal cord. To restore performance after suffering this kind of injury, surgical intervention is required.
Accidents to the Brachial Plexus Can Be Caused By:
Injuries to the Brachial Plexus at Delivery (Obstetric Brachial Plexus Injury)
During birth, infant's brachial plexus nerves, which are located in the shoulder, are in a vulnerable state. Injury to the brachial plexus is fairly common during birth, happening in about one to two out of every 1,000 births. Babies who are born vaginally during hard labour and babies whose mothers have diabetes are more likely to get this kind of damage.
Brachial plexus injuries may be more likely to happen to babies who are bigger than average when they are born. It is possible to damage the nerves in the brachial plexus that lie beneath the baby's skull when the head is stretched away from the shoulder. Brachial plexus injuries can also happen when a baby is born in the breech position, where the bottom of the baby is the first part to come out, or when a baby's labor lasts longer than usual. Shoulder dystocia is a condition that happens when the shoulder gets stuck under the pubis for a short time as the baby is being born. This can lead to injury to the brachial plexus.
Usually, injuries to the brachial plexus at birth show up in one of two ways:
Erb's palsy is often caused by damage to the upper brachial plexus nerves. This causes numbness and loss of mobility around the shoulder, as well as the inability to bend the elbow, raise an arm, or bring things to the mouth.
Klumpke's palsy is a condition that affects the lower brachial plexus and can cause a loss of motion and/or sensation in the wrist and hand. This can manifest itself in a variety of ways, including the inability to move the fingertips.
The seriousness of these wounds can differ quite a bit from case to case. Some children who were born with brachial plexus birth injuries get better on their own, but the majority of these children will get better with the help of physical and occupational therapy. To restore proper operation in a more limited population, a physical intervention will be necessary. Improved long-term outcomes are possible with earlier identification and treatment.
Accidents to an adult's brachial plexus can be caused by:
There are a variety of factors that can lead to brachial plexus injuries in adults, including the following:
- Trauma is caused by blunt force, such as that caused by slips or car collisions.
- Injuries sustained during athletic competition, particularly those sustained during collision sports such as football
- Gunshot wounds: a projectile pierces the nerves or comes very close to doing so.
- An example of medical trauma is when a nerve is severed during surgery, or when an injection or the positioning of the body during an operation causes the nerve to be injured.
- Brachial plexus invasion due to cancer.
- Radiation therapy: Damage to the nerves occurs as a result of radiation treatment.
What are the long-term consequences of sustaining an injury to the brachial plexus?
If there is a lot of damage to the brachial plexus, it might be necessary to have surgery right away to try to get the function back. If you don't have it, you could end up with a persistent disability that prevents you from feeling or using your hand or limb.
If you hurt your brachial plexus and lost feeling in your arm, you should be extra careful when working with hot items, razors, weapons, and anything else that could hurt you. It's possible that you won't even realize you're hurt if you've got a brachial plexus injury because it can prevent you from experiencing the pain of any other injury in the affected region.
Certain brachial plexus injuries can result in the condition known as Horner's syndrome. It is characterized by the injury of specific neurons in the sympathetic nervous system. This condition can cause one eyelid to droop, the pupil to get too small, and one side of the face to sweat less than the other. At the moment, there is no known way to cure Horner's syndrome. However, treating the underlying cause of the condition can sometimes help to ease its symptoms.
An injury to the brachial plexus can also cause long-lasting pain, especially if treatment is put off for a long time. It is important to work together with your neurosurgeon and physical therapist to figure out the best ways to deal with your pain.
Injuries to the brachial plexus due to trauma frequently occur in conjunction with other injuries to the neck and shoulder region, such as bone fractures and shoulder dislocations. To maximize one's chances of making a full recovery from an injury, one must approach the injury in its entirety.
References
- Brachial Plexus Injury | Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment. n.d. Brachial Plexus Injury | Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment. https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/b/brachial-plexus.
- @ClevelandClinic. n.d. Brachial Plexus Injury: What It Is, Symptoms, Treatment & Types. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22822-brachial-plexus-injury.
- Brachial Plexus Injury. 2022, December 22. Brachial Plexus Injury | Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/brachial-plexus-injuries.
- Brachial Plexus Anatomy: Overview, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply of the Brachial Plexus. 2015, August 12. Brachial Plexus Anatomy: Overview, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply of the Brachial Plexus. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1877731-overview.
- The Brachial Plexus - Sections - Branches - TeachMeAnatomy. n.d. The Brachial Plexus - Sections - Branches - TeachMeAnatomy. https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/nerves/brachial-plexus/.
- Brachial plexus. n.d. Brachial plexus: Anatomy, branches and mnemonics | Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/brachial-plexus.


As a person, I find the complex network of nerves that control movement and sensation in our arms and hands fascinating, seeing how a single injury or trauma to the brachial plexus can have so such a significant impact on our daily lives. Thanks for sharing this informative post.
True, we can not talk about the upper limb without mentioning the brachial plexus as this nerve network is so important.
Thank you for stopping by
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.